Decoding the 3/8-Inch Bolt: The Nut You Need

In the intricate world of fasteners, finding the right companions for your bolts is paramount. It's a pairing as crucial as software and hardware, where compatibility dictates functionality. This exploration focuses on the 3/8-inch bolt – a ubiquitous workhorse in construction, automotive repair, and DIY projects – and its perfect nut partner.
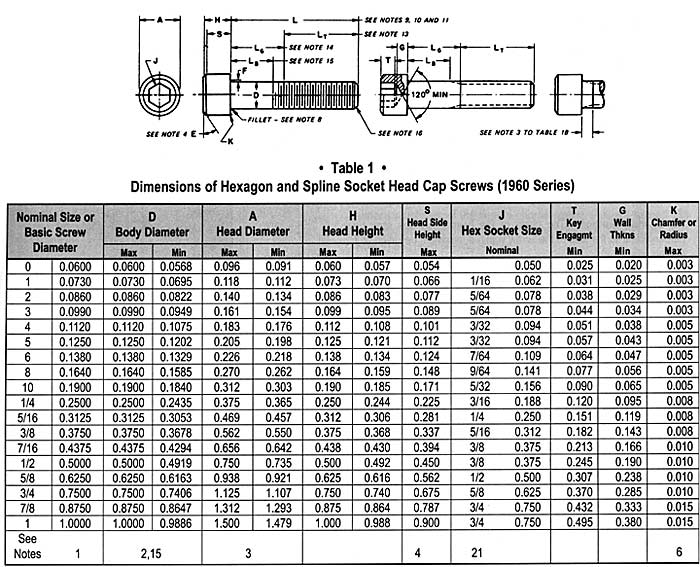
The seemingly simple question, "What size nut fits a 3/8 bolt?" opens a surprisingly nuanced discussion. While a 3/8-inch nut is the typical answer, several factors influence the true compatibility. Thread pitch, measured as threads per inch (TPI), plays a significant role. A common 3/8-inch bolt uses a 16 TPI, but variations exist, requiring a nut with a corresponding thread pitch for a secure connection.
Beyond thread pitch, the nut's material and grade also matter. Matching the bolt's material (e.g., steel, stainless steel) ensures consistent strength and corrosion resistance. The grade, a numerical rating indicating tensile strength, should align for optimal performance. Using a lower-grade nut on a high-grade bolt compromises the entire assembly.
The history of threaded fasteners dates back millennia, with evidence of early forms found in Roman architecture. The standardization of threads, however, is a more recent development. The need for interchangeability drove the adoption of unified thread standards, simplifying manufacturing and repair across industries. The 3/8-inch bolt, adhering to these standards, became a staple in modern engineering.
Correct nut and bolt pairing is essential for structural integrity. A mismatched nut can lead to stripped threads, loosening under stress, or even catastrophic failure. Understanding the nuances of thread pitch, material, and grade safeguards against these issues, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
Simply put, the thread pitch is the distance between adjacent threads. For example, a 16 TPI means there are 16 threads within one inch of the bolt length. This measurement is critical for proper engagement between the nut and bolt. A 3/8-inch-16 TPI bolt requires a 3/8-inch-16 TPI nut. Using a 24 TPI nut on a 16 TPI bolt will result in a cross-threaded connection, potentially damaging both components.
Benefits of using the correct size nut:
1. Secure fastening: A proper fit ensures the nut and bolt engage fully, distributing load evenly and preventing loosening under vibration or stress.
2. Preventing damage: Matching thread pitches prevents cross-threading, safeguarding both the nut and bolt from damage. This avoids costly repairs and replacements.
3. Structural integrity: Using the correct nut size ensures the assembled components can withstand intended loads, maintaining the overall structural integrity.
Action Plan for Identifying the Correct Nut:
1. Measure the bolt diameter: Use a caliper or ruler to confirm the 3/8-inch diameter.
2. Determine the thread pitch: Count the threads per inch or use a thread gauge.
3. Match the material and grade: Select a nut made of the same material and grade as the bolt.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Nut Materials
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | High strength, readily available | Susceptible to rust |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, strong | More expensive |
Best Practices:
1. Use a torque wrench to tighten the nut to the manufacturer's specified torque.
2. Lubricate the threads to reduce friction and ensure accurate torque readings.
3. Avoid over-tightening, which can damage the threads or the fastened materials.
4. Inspect the nut and bolt for damage before use.
5. Use appropriate locking mechanisms (e.g., lock washers, nylon insert nuts) for applications subject to vibration.
FAQs:
Q: Can I use a metric nut on a 3/8-inch bolt? A: No, metric and imperial threads are incompatible.
Q: What is the difference between a coarse and fine thread? A: Coarse threads have fewer threads per inch than fine threads.
Q: What is a lock nut? A: A lock nut has a mechanism to prevent it from loosening.
Q: How can I tell if a nut is the correct size? A: It should thread onto the bolt smoothly and fully engage.
Q: Where can I buy the correct nut? A: Hardware stores, automotive parts stores, and online retailers.
Q: What if I can't find a nut with the correct thread pitch? A: Consult a fastener specialist.
Q: What are the different grades of nuts and bolts? A: Grades indicate tensile strength, with higher numbers denoting greater strength.
Q: How do I determine the correct torque for a 3/8-inch bolt? A: Consult a torque chart or the manufacturer's specifications.
Tips and Tricks:
Keep a thread gauge handy to quickly determine thread pitch. Organize your fasteners by size and type for easy access.
Understanding the relationship between a 3/8-inch bolt and its corresponding nut is crucial for anyone working with fasteners. The correct nut ensures a secure and reliable connection, preventing potential problems ranging from minor loosening to significant structural failure. By paying attention to thread pitch, material, and grade, and following best practices for tightening and installation, you can achieve optimal performance and longevity in your projects. Investing time in understanding these fundamental principles of fastening pays dividends in safety, efficiency, and the satisfaction of a job well done. This knowledge empowers you to build, repair, and create with confidence, knowing that the smallest components, like the humble nut and bolt, are working in perfect harmony.
Conquer espn nfl pick em week 7 score big and brag loud
Ron jon surf shop cocoa beach experience
Spice up your life the ultimate guide to kitchen feng shui