The Magic of AC to DC Conversion

Have you ever wondered how your phone charges from the wall socket? The answer lies in a clever piece of technology called an AC to DC signal converter. These unsung heroes of the electronics world silently transform the alternating current (AC) from your power outlet into the direct current (DC) that powers most electronic devices. This transformation is essential for everything from charging our phones to powering our laptops and running complex industrial machinery.
AC to DC conversion, or rectification, is a fundamental process in electrical engineering. AC power, characterized by its fluctuating voltage, is efficient for long-distance transmission. However, most electronic components require a stable, unidirectional current, which is precisely what DC provides. This is where the AC to DC signal converter steps in, bridging the gap between the power source and the device.
The history of AC to DC conversion is intertwined with the development of electricity itself. Early experiments with electricity involved primarily DC, but with the advent of AC power transmission in the late 19th century, the need for efficient rectification became apparent. Early AC to DC converters relied on devices like rotary converters and mercury-arc valves. The invention of the solid-state diode revolutionized the field, leading to the compact and efficient converters we use today.
The significance of AC/DC transformation is hard to overstate. Imagine a world without these converters. Our laptops, smartphones, televisions, and countless other devices would be tethered to bulky batteries or require entirely different power systems. The ability to seamlessly convert AC power to DC has enabled the proliferation of portable and convenient electronic devices that are integral to our modern lives.
One of the main challenges in AC to DC conversion is efficiency. Converting energy from one form to another inevitably involves some losses. Engineers constantly strive to improve the efficiency of AC to DC signal converters to minimize energy waste and reduce heat generation. Modern converters utilize sophisticated switching techniques and advanced semiconductor materials to achieve high levels of efficiency.
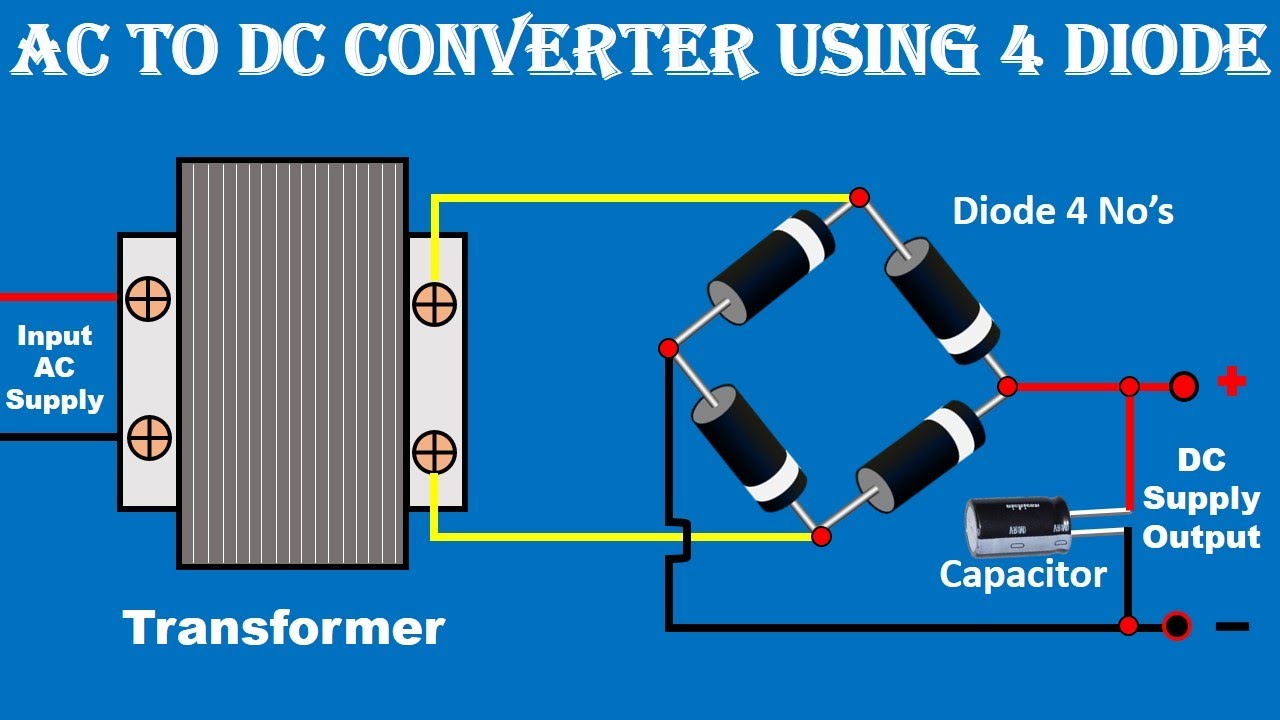
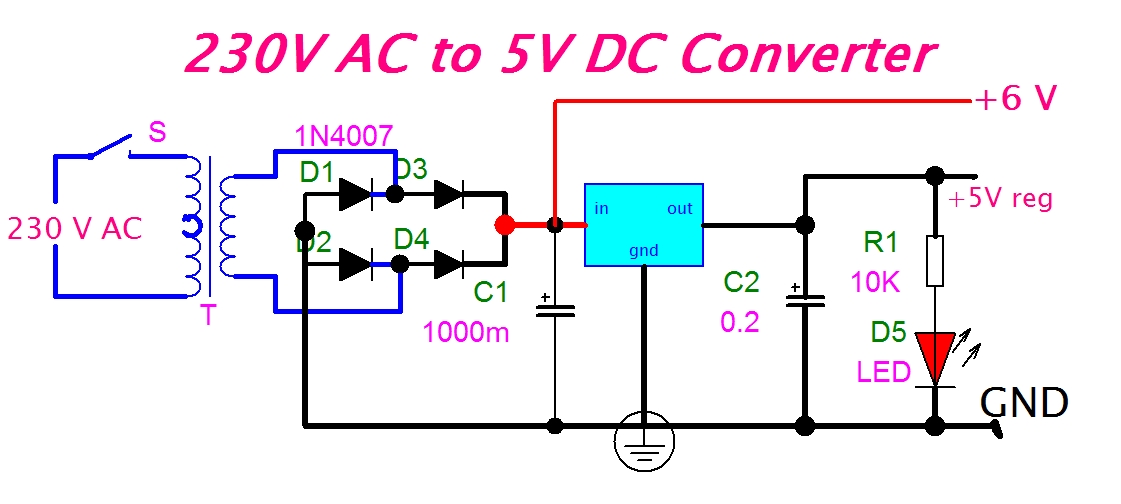
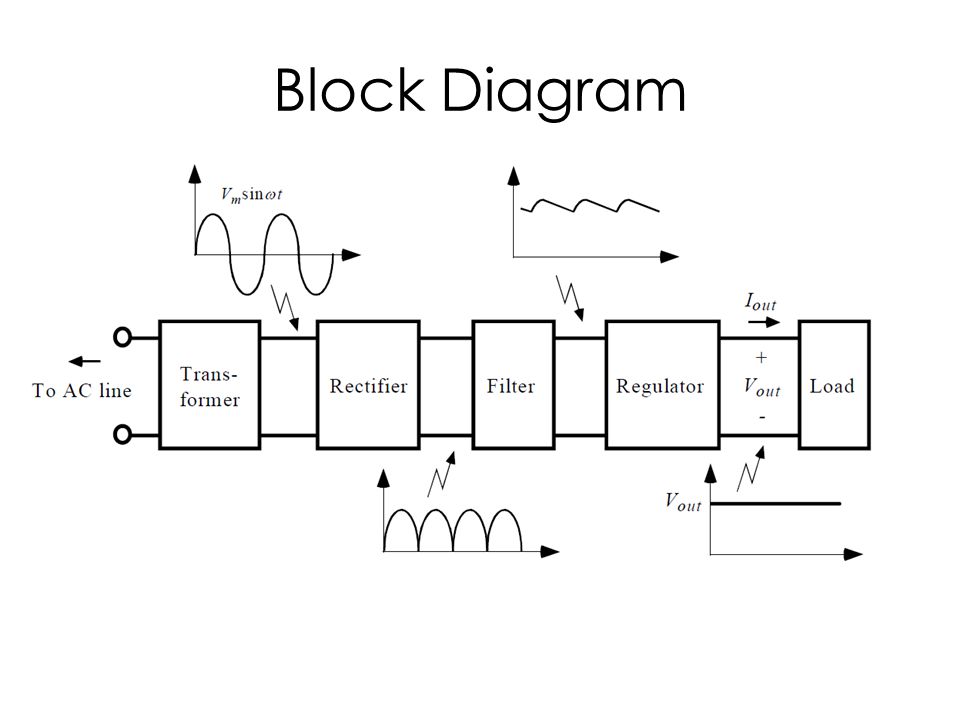
A simple example of an AC to DC converter is the adapter used to charge your phone. Inside this small device, a transformer reduces the high voltage AC from the outlet. Then, diodes rectify the AC into pulsating DC, and finally, a filter smooths the pulsating DC into a stable output voltage suitable for your phone's battery.
One benefit of AC/DC converters is portability. By enabling devices to run off standard AC power, they eliminate the need for specialized DC power sources, making them more portable and convenient.
Another advantage is safety. AC/DC converters often incorporate isolation circuits that protect users from electrical shocks by separating the low-voltage DC output from the high-voltage AC input.
Lastly, AC/DC converters allow for voltage regulation, ensuring that devices receive a stable and consistent voltage regardless of fluctuations in the AC supply.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AC to DC Converters
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Portability | Can be inefficient depending on the design |
| Safety through isolation | Can generate heat, especially at high power levels |
| Voltage Regulation | Can be sensitive to fluctuations in the AC supply |
Five best practices for implementing AC/DC converters include proper heat management, choosing the right converter topology for the application, using high-quality components, implementing appropriate filtering, and ensuring proper grounding.
Five real-world examples of AC to DC converters include laptop chargers, phone adapters, power supplies for desktop computers, solar inverters, and DC motor drives.
One challenge is dealing with ripple voltage in the DC output. Solutions include using larger filter capacitors or more advanced filtering techniques. Another challenge is maintaining efficiency at high power levels. This can be addressed by using more efficient converter topologies and advanced switching techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions about AC/DC converters include: What is the difference between AC and DC? How does an AC/DC converter work? What are the different types of AC/DC converters? What is rectification? What is the role of a diode in rectification? What is the purpose of a filter in an AC/DC converter? How do I choose the right AC/DC converter for my application? How do I troubleshoot an AC/DC converter?
Tips and tricks for working with AC/DC converters include ensuring proper ventilation for heat dissipation, using a multimeter to check the output voltage, and consulting datasheets for specific converter specifications.
In conclusion, AC to DC signal converters are essential components in countless electronic devices. Their ability to transform alternating current into direct current empowers us to use portable electronics, run complex machinery, and harness renewable energy sources like solar power. Understanding the principles of AC/DC conversion and implementing best practices ensures safe and efficient operation of these ubiquitous devices. From the simple phone charger to sophisticated industrial power supplies, AC to DC signal converters play a vital role in our technology-driven world. The ongoing development of more efficient and compact converters promises to further enhance the performance and portability of electronic devices in the future, driving innovation and shaping the way we interact with technology. Explore further by researching different converter topologies and learning about the latest advancements in power electronics.
Refreshing spaces with behr sail cloth a soft versatile paint color
Finding the perfect jonesboro ar rental home
Unlocking the neighborhood exploring mister rogers friends and the enigmatic 1508