Understanding the Medicare Fee-for-Service Program
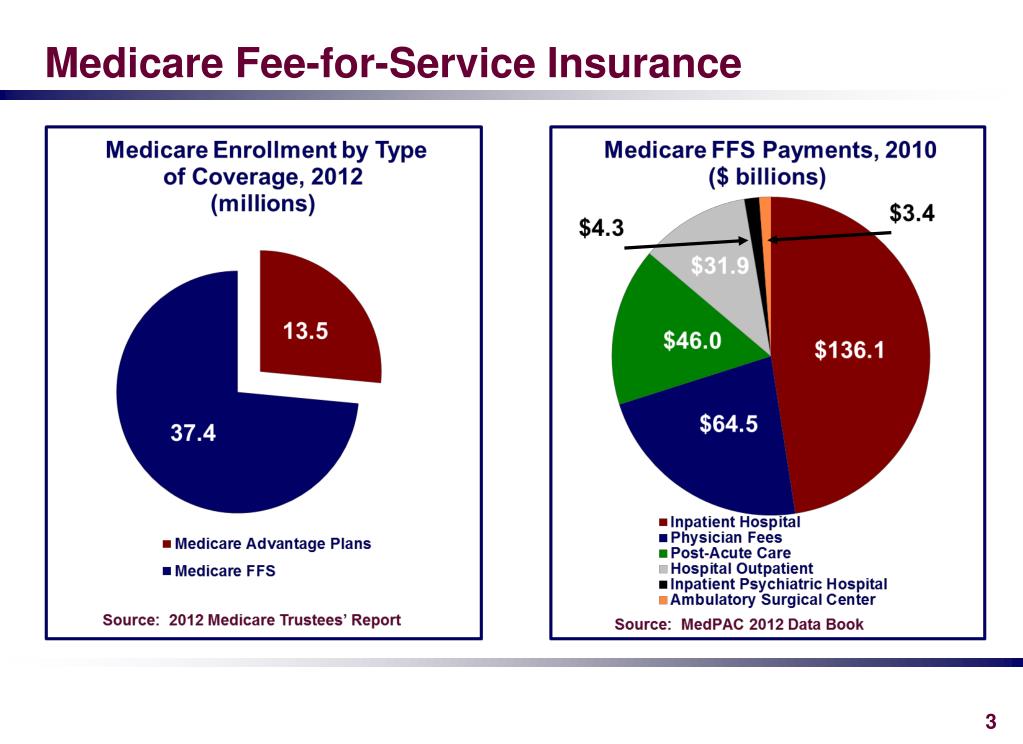
Navigating the complexities of Medicare can feel overwhelming. One of the foundational options within Medicare is the Fee-for-Service program, often referred to as Original Medicare. This traditional payment structure covers a wide range of medical services, offering flexibility and choice in healthcare providers. But how exactly does it work, and is it the right choice for you?
The Medicare Fee-for-Service plan allows beneficiaries to receive healthcare services from any doctor or hospital that accepts Medicare assignment. This means providers agree to accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment for covered services. This freedom to choose your healthcare providers is a key attraction for many individuals. It provides a sense of control and familiarity, especially for those with established relationships with their doctors.
Understanding the nuances of the Medicare Fee-for-Service payment system is crucial for maximizing your benefits. Essentially, Medicare pays a set amount for each covered service or procedure. You typically pay a deductible and coinsurance, with Medicare covering the remaining portion. This predictable cost structure allows beneficiaries to anticipate their out-of-pocket expenses, facilitating better budget management for healthcare costs.
Historically, the Medicare Fee-for-Service structure has been the cornerstone of the Medicare program since its inception in 1965. It provides a framework for accessing a broad spectrum of healthcare services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and preventive care. Over the years, the program has evolved to address changing healthcare needs and rising costs, reflecting a commitment to ensuring access to quality medical care for seniors and individuals with disabilities.
While the traditional Medicare Fee-for-Service model offers significant advantages, it’s important to consider some potential drawbacks. One key consideration is the absence of an out-of-pocket maximum. This means your expenses could theoretically be unlimited, which can be a concern for individuals with chronic conditions or those who require extensive medical care. Supplementing Original Medicare with a Medigap policy is a common strategy to mitigate this risk.
The Medicare Fee-for-Service program consists of Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance). Part A generally covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, some home health care, and hospice care. Part B covers services like doctor visits, outpatient care, preventive services, and some medical equipment. Understanding these distinct components is fundamental to effectively utilizing your Medicare benefits.
For example, if you require a hospital stay due to pneumonia, Part A of your Medicare Fee-for-Service plan would typically cover the associated costs, subject to deductibles and coinsurance. Subsequent follow-up visits with your doctor to monitor your recovery would be covered under Part B.
One of the benefits of a Medicare Fee-for-Service plan is the vast network of providers. You have the freedom to choose any doctor or hospital that accepts Medicare, providing flexibility and access to specialists across the country. This extensive network is a major advantage for individuals who travel frequently or have specific healthcare needs.
Another advantage is the simplicity of the claims process. Medicare directly processes claims with participating providers, eliminating the need for submitting claims yourself in most cases. This streamlined process reduces administrative burden and simplifies the healthcare experience. An additional benefit is the predictable cost structure, which helps beneficiaries anticipate their out-of-pocket expenses for covered services.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Medicare Fee-for-Service
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Large provider network | No out-of-pocket maximum |
| Simple claims process | May require supplemental coverage |
| Predictable cost structure | Doesn't cover all healthcare expenses (e.g., dental, vision) |
Frequently Asked Questions about Medicare Fee-for-Service:
1. What is Medicare assignment? Answer: Accepting Medicare assignment means a provider agrees to accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment for covered services.
2. What is the difference between Part A and Part B? Answer: Part A covers hospital insurance, while Part B covers medical insurance.
3. How do I find a doctor who accepts Medicare? Answer: You can use the Medicare Physician Compare tool online.
4. What is a Medigap policy? Answer: A Medigap policy helps cover some of the out-of-pocket costs not covered by Original Medicare.
5. How do I enroll in Medicare Fee-for-Service? Answer: You can enroll through the Social Security Administration.
6. Does Medicare Fee-for-Service cover prescription drugs? Answer: No, prescription drug coverage is provided through separate Medicare Part D plans.
7. Can I travel outside the U.S. with Medicare Fee-for-Service? Answer: Generally, Original Medicare offers limited coverage outside the U.S.
8. What are some tips for managing costs with Medicare Fee-for-Service? Answer: Consider a Medigap policy, shop around for durable medical equipment, and take advantage of preventive services.
In conclusion, the Medicare Fee-for-Service program, also known as Original Medicare, represents a significant pillar of the American healthcare system. Its flexibility in provider choice, predictable cost structure, and comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical services make it a valuable option for many beneficiaries. However, understanding its limitations, such as the absence of an out-of-pocket maximum and the need for supplemental coverage for certain expenses like prescription drugs, is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare. By carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages and actively engaging in managing your Medicare benefits, you can effectively leverage the Fee-for-Service program to access the quality care you need while maintaining control over your healthcare journey. Consider speaking with a Medicare specialist or utilizing online resources like Medicare.gov to further explore your options and choose the best plan for your individual circumstances. Don't hesitate to reach out to trusted sources for assistance navigating the Medicare landscape and securing the healthcare you deserve.
Dominate your draft unlocking fantasy football running back value
Unleash your inner artist learn clown drawing step by step
The curious case of cat memes on whatsapp







