Unlocking the Magic: How Solenoid Valves Work

Ever wonder how your washing machine fills with just the right amount of water or how your sprinkler system knows when to turn on? The answer often lies in a small but mighty device: the solenoid valve. These ingenious components are the unsung heroes of countless systems, quietly controlling the flow of liquids and gases. Let's delve into the fascinating world of solenoid valves and discover the principles behind their operation.
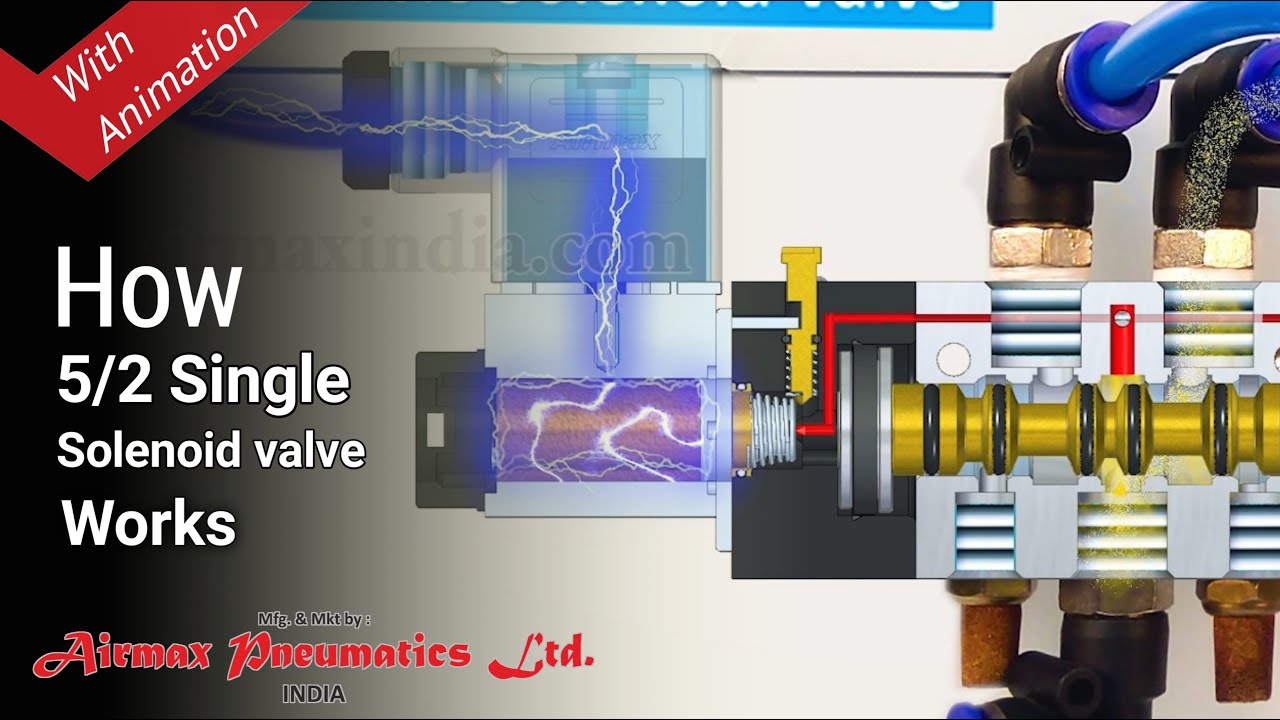
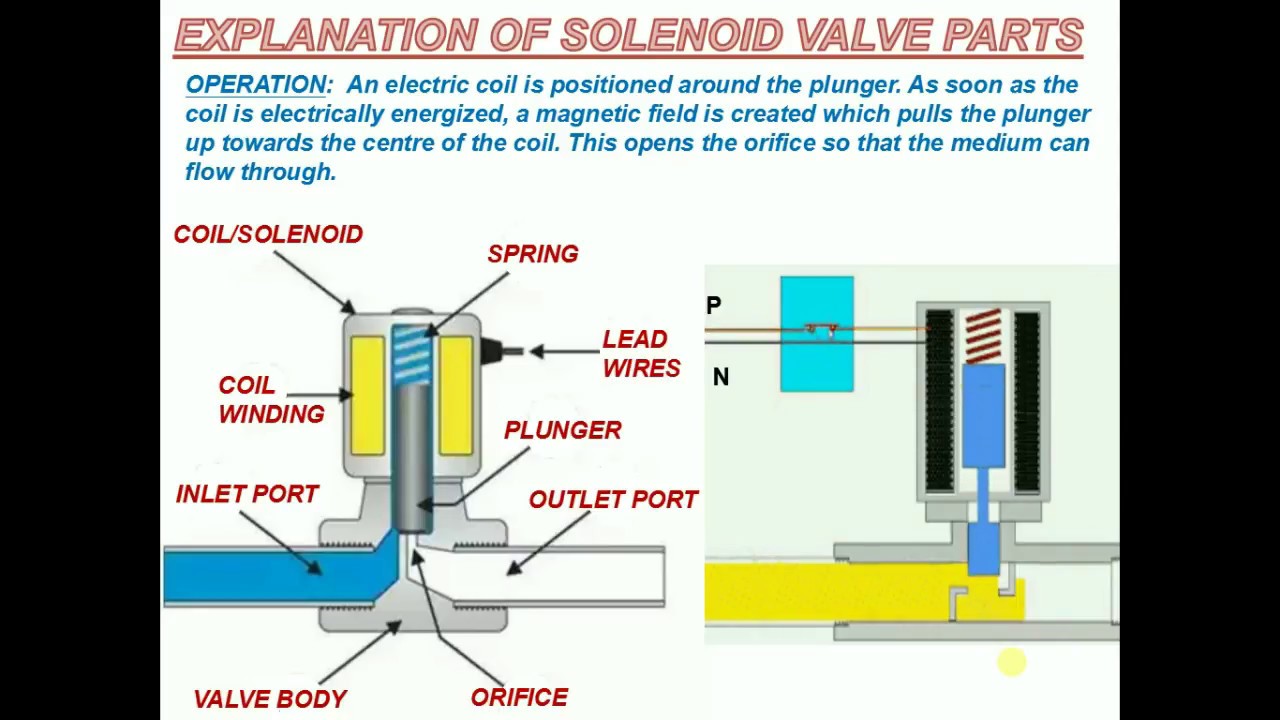
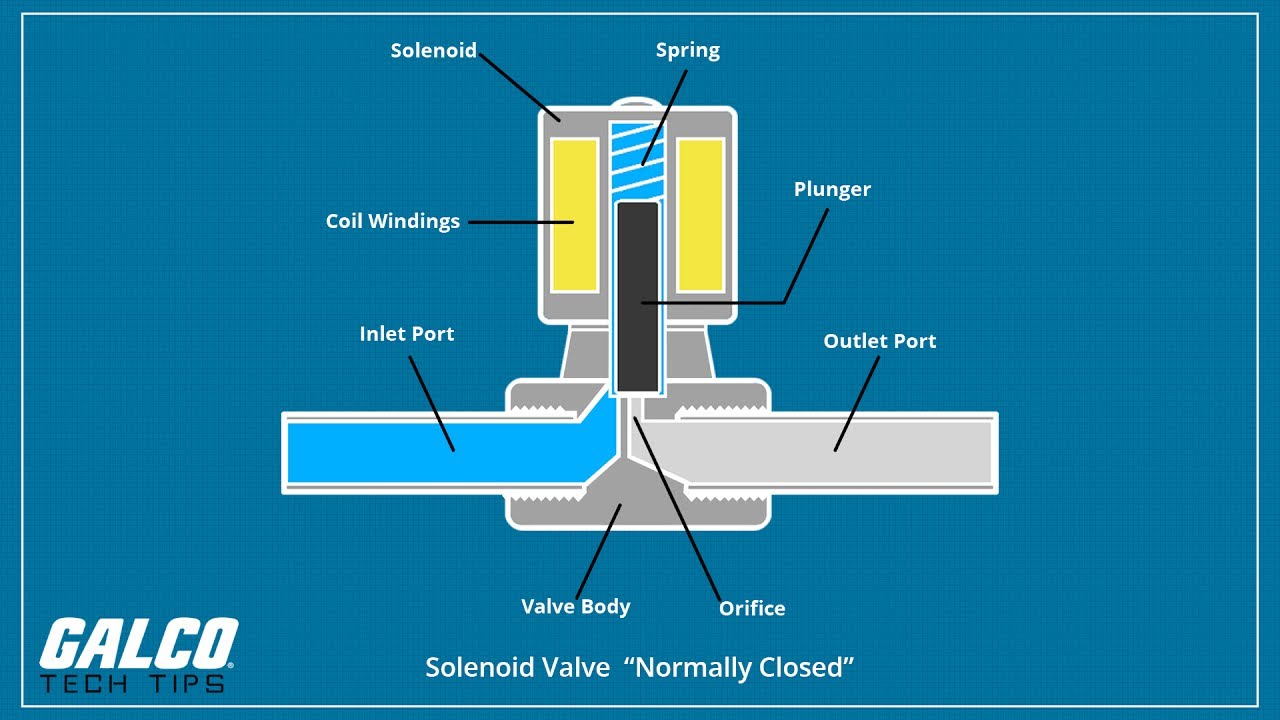
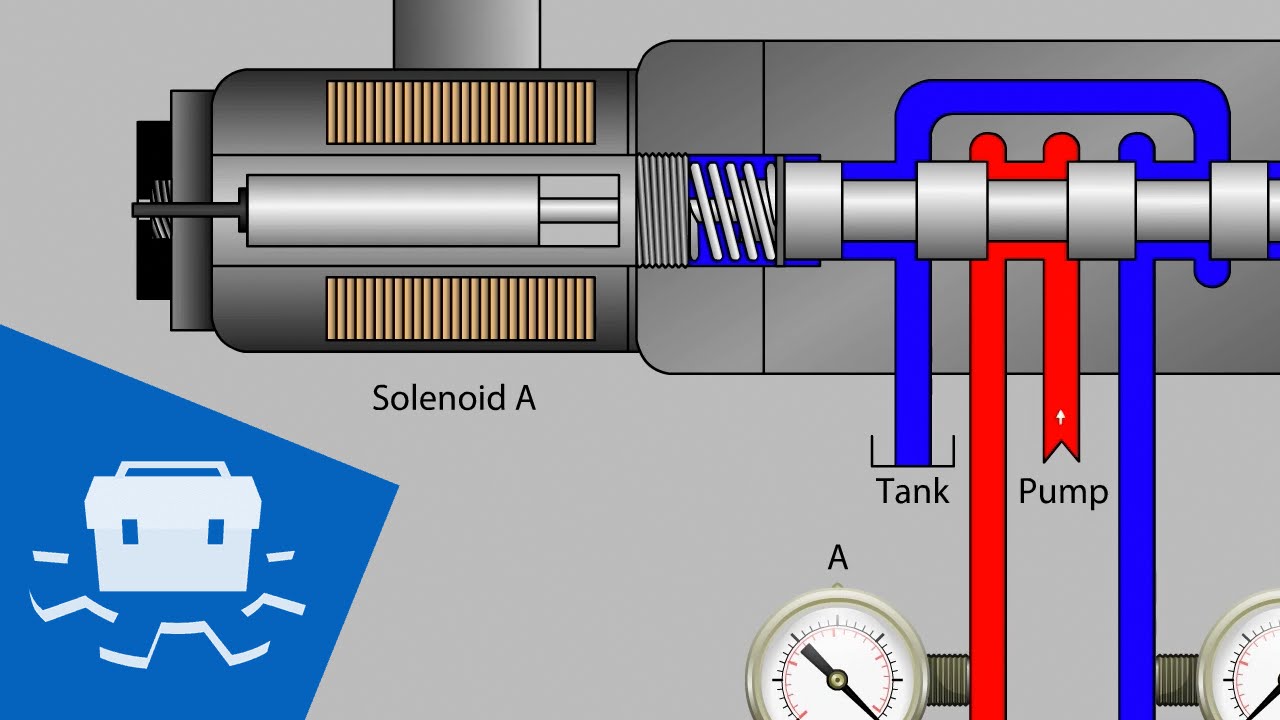
A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated valve. In simpler terms, it uses electricity to control the flow of a fluid. When energized, the solenoid creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger or diaphragm, opening or closing the valve. This allows for precise and automated control of fluid flow, making solenoid valves indispensable in a wide range of applications.
Imagine a tiny gatekeeper regulating the passage of liquids or gases. That's essentially what a solenoid valve does. Its operation relies on the principles of electromagnetism. An electric current passing through a coil of wire creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field then interacts with a ferromagnetic plunger or diaphragm, causing it to move and either open or close the valve orifice, thus controlling fluid flow.
The history of solenoid valves dates back to the early 20th century, with initial applications in industrial automation. As technology advanced, solenoid valves became smaller, more efficient, and more reliable, expanding their use into diverse fields like irrigation, automotive, medical equipment, and household appliances.
Understanding solenoid valve function is crucial for anyone working with fluid control systems. From ensuring efficient irrigation to maintaining precise medical equipment operation, these valves play a critical role. Common issues like leaks, sticking plungers, or electrical malfunctions can disrupt system performance, highlighting the importance of proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Solenoid valves come in two main types: direct-acting and pilot-operated. Direct-acting valves use the magnetic force directly to open or close the valve. Pilot-operated valves use a small pilot valve to control the flow of a larger main valve, allowing for the control of higher pressures and flow rates.
Three key benefits of utilizing solenoid valves include precise control, automation, and reliability. Precise control allows for accurate fluid dispensing, as seen in washing machines and coffee makers. Automation simplifies complex processes, such as automated irrigation systems. Reliability ensures consistent and dependable performance in critical applications like medical equipment.
When selecting a solenoid valve, consider factors like fluid type, pressure requirements, and flow rate. Ensure compatibility with the system's electrical specifications and environmental conditions. Regular inspection and maintenance, including cleaning and checking for leaks, can prevent malfunctions and extend the valve's lifespan.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solenoid Valves
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Precise control of fluid flow | Can be sensitive to pressure fluctuations |
| Fast response time | Potential for clogging or contamination |
| Easy to automate | Requires a power source |
Best practices for implementing solenoid valves include proper sizing, selecting the correct valve type, ensuring proper installation, and implementing regular maintenance schedules. Careful consideration of these factors contributes to optimal performance and longevity.
Examples of solenoid valve applications include controlling water flow in washing machines, regulating gas flow in heating systems, controlling air pressure in pneumatic systems, dispensing liquids in vending machines, and managing irrigation systems.
Challenges related to solenoid valve operation can include clogging due to debris, leaks caused by worn seals, electrical malfunctions due to power surges, and sticking plungers due to corrosion. Solutions involve regular cleaning, replacing worn parts, installing surge protectors, and using appropriate lubricants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a solenoid valve?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated valve that controls fluid flow.
How does a solenoid valve work?
It uses an electromagnetic field to move a plunger, opening or closing the valve.
What are the types of solenoid valves?
Direct-acting and pilot-operated.
What are the benefits of using solenoid valves?
Precise control, automation, and reliability.
What are common issues with solenoid valves?
Leaks, sticking plungers, and electrical malfunctions.
How do I choose the right solenoid valve?
Consider fluid type, pressure, flow rate, and electrical specifications.
How do I maintain a solenoid valve?
Regular cleaning, inspection, and replacement of worn parts.
Where are solenoid valves used?
Washing machines, irrigation systems, heating systems, and more.
Tips and tricks for working with solenoid valves include ensuring proper grounding, using appropriate wiring, and protecting the valve from extreme temperatures and moisture.
In conclusion, solenoid valves are essential components in a vast array of systems, enabling precise and automated fluid control. Understanding their operation, benefits, and potential challenges is crucial for anyone working with fluid control systems. From everyday appliances to complex industrial processes, solenoid valves play a critical role in ensuring efficiency, reliability, and precise control. By following best practices for implementation and maintenance, you can ensure the optimal performance and longevity of these versatile devices. Investing time in learning about solenoid valve functionality will undoubtedly empower you to troubleshoot issues effectively and maximize the benefits of these indispensable components in countless applications. Take the time to delve deeper into the specifics of solenoid valve technology, and you’ll be well-equipped to manage any fluid control challenge that comes your way.
Decoding feline skin mysteries a closer look at cat skin rashes
Unlocking wheel wellness your guide to discount tire lug nut torque
Decoding the language of circuits electronic schematic symbols